Summary: Cordyceps is a mushroom used in Traditional Chinese Medicine that is touted to be anti-aging and pro-vitality; these quite vague claims have not yet been looked at in human interventions. It can regulate testicular testosterone production, but has complex mechanisms.
Introduction
What is Cordyceps Militaris Mushroom?
According to the theory of Chinese medicine, C. sinensis is sweet in taste and neutral in nature, and it can replenish the kidney, soothe the lung, stop bleeding, and eliminate phlegm. The fungus C. sinensis has been used for the treatment of fatigue, cough, hyposexuality, asthenia after severe illness, renal dysfunction, and renal failure (State Pharmacopoeia Commission of PRC 2005). In China, it is found in the soil of prairies at elevations of 3500–5000 m, mainly in the provinces of Qinghai, Tibet, Sichuan, Yunnan, and Gansu. In China, C. sinensis has been known and used as a remedy for more than 300 years. It was first recorded in Ben Cao Bei Yao by Wang Ang in 1694, and the Italian scholar Saccardo named the Cordyceps found in China officially as Cordyceps sinensis (Berk.) Sacc. in 1878; this nomenclature has been used ever since. [R]
Cordyceps vs. Reishi vs. Lion’s Mane
Along with other mushrooms like the Chaga mushroom and turkey tail mushroom, cordyceps, reishi and lion’s mane are three of the most popular medicinal mushrooms on the market. That being said, there are plenty of similarities between these three unique types of mushrooms as well as several things that set them apart.
Reishi mushrooms have been associated with an extensive list of health benefits, ranging from improved liver function to enhanced immunity in human and animal studies. Available in
And while both reishi and cordyceps mushrooms are most commonly found in supplement form, lion’s mane is an edible mushroom that can be purchased from specialty grocery stores and used to bump up the benefits of your favorite recipes. Like other types of medicinal mushrooms, lion’s mane mushroom is high in inflammation-busting antioxidants and can help maximize immunity to support better health. However, it’s also been shown to improve brain function and protect against stomach ulcers in animal models.
Dr.Axe
History
The ecosystem of C. sinensis has been terribly affected by the restriction of habitat and over- exploration. Although the Ordinance of Resources Protection on Wild Herbal Medicine was issued in 1987, the yield of natural C. sinensis is still decreasing. It was reported based on a survey conducted during June–July 2007 that the yield of natural C. sinensis decreased by more than 90% in the last 25 years. The price rocketed to more than 200,000 Renminbi (RMB)/kg (approximately US$25,000) in 2007 (Feng, Yang, and Li 2008), and its usage was limited during the past decade by its limited supply. [R]
Due to the rarity and outstanding curative effects of C. sinensis, some natural substitutes such as C. militaris, C. liangshanensis, C. gunnii, and C. cicadicola have been sold in markets (Yang et al. 2009). In addition, several cultured mycelia of C. sinensis and C. militaris fungi have become the main substitutes of the natural species as commercial products, and 50 medicines and two dietary supplements related to cultured Cordyceps have been approved by the State Food and Drug Administration of China since 2002 (Feng, Yang, and Li 2008). For example, JinShuiBao capsule, the commercial product of Cs-4 (Paecilomyces hepialid, a standardized mycelium of C. sinensis), has been used in clinics throughout China. This product generates several million U.S. dollars every year. Synnematum sinensis, Cephalosporium sinensis, Gliocladium roseum, and Mortierella hepialid, the fungus strains isolated from natural C. sinensis, have also been subjected to large- scale fermentation and are used as commercial products (Cheung, Li, and Tsim 2005). Therefore, much effort has been invested in studying the evaluation of the quality, pharmacological activities, and clinical efficacies of natural and cultured cordyceps. In this chapter, we focus on the bioactivities, action mechanisms, and active ingredients of cordyceps, both natural and cultured. [R]
Cordyceps sinensis (C sinensis) is a well-known, traditional, Chinese medicinal mushroom, valued for its beneficial properties for human health. C sinensis has been reported to have immunomodulatory, anticancer, anti aging, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity. [R]
Cordyceps is a mushroom traditionally used to treat sexual dysfunction and fertility in Chinese medicine, as well as a general sexual tonic and libido/performance enhancer. [1]
This mushroom belongs to phylum Ascomycota, the sub-phylum Ascomycota and the class Clavicipitaceae; which as a whole is seen as medicinal.
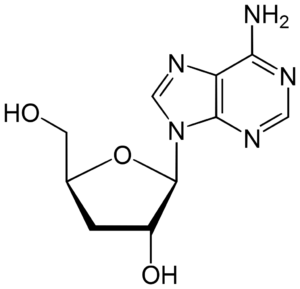
The most commonly used species is Sinensis, which is a Cordyceps to be shown to contain the bioactive compound Cordycepin (3′-deoxyadenosine). It is also present in Militaris and Kyushuensis.
Isolation of Cordycepin dates back to 1950, first discovered in Militaris. Cordycepin is known as a nucleotide analogue, due to its structural similarities to adenosine.
Cordyceps possesses a potent anti-oxidative effect. The anti-oxidative effects of Cordyceps come mostly from the polysaccharide content, and is equally potent between the Mycelium and the fruiting body of Cordyceps.
Cordyceps (also known as Cordyceps Sinensis, Cordyceps Militaris, Caterpillar Fungus, Caterpillar Mushroom, Summer grass-winter worm, Totsu kasu, Yarchakunbu, Aweto) is a form of traditional chinese medicine that benefits its user by boosting testosterone and supports anti-aging and longevity. It is also widely used for its libido and sexual health benefits.
Cordyceps militaris is a species of mushroom in the family Clavicipitaceae which has been used in traditional Chinese and Tibetan medicine for centuries. These interesting parasitic fungi usually use insects and arthropods as hosts. As their mycelium grows, it takes over the host’s tissues and long club-like fruiting bodies eventually emerge individually or in cluster form. Cordyceps Militaris is just one species in the family, but is well-known for its aggressive takeover of its host as well as for its purported health benefits.
Cordyceps Militaris historically has been used as an aphrodisiac, and was first documented in a 15th-century Tibetan text. However, Cordyceps militaris Mushroom Capsules today are sometimes used for a variety of health issues.
Benefits and Effects
What Are Cordyceps Mushroom Benefits?
Boosts Exercise Performance
Cordyceps have been shown to improve measures of exercise performance in older and younger adults.
In a study conducted by the Center for Human Nutrition at the University of California, Los Angeles, where 20 health adults aged 50 to 75 were receiving 333 mg vs placebo 3 times a day for 12 weeks, the result was the following:
After receiving Cs-4 for 12 weeks, the metabolic threshold (above which lactate accumulates) increased by 10.5% from 0.83 ± 0.06 to 0.93 ± 0.08 L/min (p < 0.02) and the ventilatory threshold (above which unbuffered H+ stimulates ventilation) increased by 8.5% from 1.25 ± 0.11 to 1.36 ± 0.15 L/min. Significant changes in metabolic or ventilatory threshold were not seen for the subjects in the placebo group after 12 weeks, and there were no changes in V̇o2 max in either group. [R]
Promotes Longevity and Anti-Aging
Several studies have found that Cordyceps increase antioxidants in aged mice, helping improve memory and sexual function. Antioxidants are molecules that fight cell damage by neutralizing free radicals, which can otherwise contribute to disease and aging.
The following study The study was conducted at the Center for Biological Research, University of Belgrade. The participants were 6 individuals, 2 males and 4 females, between the ages of 20 and 45 years old. The outcome measures of the studies were the following:
For the posttreatment, the CS extract exhibited antigenotoxic potential by attenuating H2O2-induced DNA damage at all concentrations tested. The evaluation of repair kinetics showed a decrease in DNA-damaged cells 15 min after the application of the CS extract, reaching a maximum potency after 45 min. Conclusions • The results indicated that C sinensis can be used as a postapplicative agent that counteracts the effect of oxidative stress. The resulting reduction in DNA damage might be related to its scavenging properties and stimulation of DNA repair. [R]
Helps Fight Inflammation
Research has shown that when human cells are exposed to Cordyceps, special proteins that increase inflammation in the body become suppressed. Thanks to these potential effects, researchers believe Cordyceps may serve as a useful anti-inflammatory supplement or drug.
A study by the College of Pharmacy, Sookmyung Women’s University in Seoul has found to contain acute anti-inflammatory activity, which was evaluated using the carrageenin-induced edema, and also strong antinociceptive activity in writhing test. CME and FBE contain potent inhibitory activity on the chick embryo chorioallantoic membrane (CAM) angiogenesis in a dose-dependent manner.
In brief, we demonstrate that Cordyceps militaris possesses anti-inflammatory and antinociceptive activities, and related antioxidant, anti-angiogenic, and NO production-inhibitory activities. [R]
Anti-Tumor and Fights Cancer in Several Pathways
Due to the limitations of surgery and radiotherapy and the side effects of chemotherapy, there is increasing interest in developing antitumor drugs from natural products. Studies have shown that cordyceps has antitumor activity in various cancers through several pathways. Both natural and cultured cordyceps have demonstrated antitumor effects [R]
Mechanism of Action
How Do Cordyceps Work?
Cordyceps might improve immunity by stimulating cells and specific chemicals in the immune system. It may also have activity against cancer cells and may shrink tumor size, particularly with lung or skin cancers.
Dosage
How To Take Cordyceps Mushrooms?
The dosage commonly used in human research is 1,000–3,000 mg per day. This range is not associated with side effects and has been found to have certain health benefits.
There is no indication if this is the optimal dose or not, and it is uncertain if this dosage is even effective as some of the research has come back null.
The appropriate dose of cordyceps depends on several factors such as the user’s age, health, and several other conditions. At this time there is not enough scientific information to determine an appropriate range of doses for cordyceps. Keep in mind that natural products are not always necessarily safe and dosages can be significant.
A little more on the explanation from Nootropics Depot:
In terms of comparing Cordyceps dosages, it is essential to remember that the 10:1 extract isn’t technically 10 times stronger than the 1:1 extract. With this in mind, our label recommends 1 gram (or 1000mg) of the 10:1 extract, which is the same dosage for the 1:1 extract. However, anecdotally, the 10:1 extract is quite a bit more stimulating so 250-500mg may be adequate as well. Many people prefer to split their 1:1 dosage into two 500mg doses spread out over the day.
This is especially true for those that can get minor stomach upset with higher dosages of Cordyceps. Our Cordyceps capsules are 500mg of our 1:1 extract in each capsule. The 10:1 seems to be stronger in some aspects, but also smoother in others. Many people find that a single 250mg dose is adequate for the 10:1. As always, this all comes down to your personal preference and what works best for you.
Side Effects
What Are Cordyceps Mushrooms Side Effects?
Cordyceps is generally safe for most people when taken appropriately by mouth, short-term.
The long history of use in Traditional Chinese Medicine suggests they are nontoxic. Moreover, the Chinese government approved the use of cordyceps for use in hospitals and regards it as a safe, natural drug. [R]
WebMD suggests caution and prevention of usage for the following cases:
Pregnancy and breastfeeding:
There is not enough reliable information about the safety of taking cordyceps if you are pregnant or breastfeeding. Stay on the safe side and avoid use.
Multiple sclerosis (MS), lupus (systemic lupus erythematosus, SLE), rheumatoid arthritis (RA), or other conditions: Cordyceps might cause the immune system to become more active. This could increase the symptoms of auto-immune diseases. If you have one of these conditions, it’s best to avoid using cordyceps.
Bleeding disorders: Cordyceps might slow blood clotting. Taking cordyceps might increase the risk of bleeding in people with bleeding disorders.
Surgery: Using cordyceps might increase the risk of bleeding during the operation. Stop taking cordyceps 2 weeks before surgery.
Conclusion
Cordyceps are well known in Traditional Chinese Medicine and have been used for centuries to treat many health ailments.
Though the fungi show promise in many areas, there’s little research on their effects in humans. Thus, more research is needed before experts can make any recommendations.
Animal and lab studies suggest Cordyceps have the potential to improve heart health and fight inflammation, cancer, diabetes and aging. However, many of these studies are poor quality, and the results cannot be extended to humans.
Nevertheless, there have been human studies on Cordyceps’ effects on exercise performance. The fungi have been found to potentially boost energy and oxygen use during exercise.
If you choose to take Cordyceps supplements, make sure they’ve been tested by a third-party organization for purity and quality.
Back to Nootropics Information homepage.